
论文DOI: 10.1007/s00704-021-03556-6
Abstract: Under the background of global warming, extreme precipitations had caused important issues, and the spatiotemporal precipitation of the main water resource (MWR) area of the Belt and Road (BR) Initiative had complex conditions. Therefore, observed daily precipitation data from 351 meteorological stations were selected to analysis temporal and spatial characteristics in extreme precipitations. The Mann-Kendall trend test was utilized to detect trends of extreme precipitation indices which were derived from the Expert Team on Climate Change Detection and Indices (ETCCDI), and the periodical characteristics of 4 typical extreme precipitation indices were calculated using wavelet analysis. In order to further analyze the relationship between extreme precipitation indices and global climate anomalies, the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) and Arctic Oscillation (AO) were selected as climate indices to investigate teleconnections between extreme precipitation indices and atmospheric oscillations. Our results revealed that (1) The climate in the MWR had become more humid, and the frequency and intensity of extreme precipitation had shown positive trend; (2) 4 typical extreme precipitation indices exhibited multiple and overlapping cycles, while 23-32 year cycles were universal; (3) the teleconnection between large scale circulation and extreme precipitation of MWR varied not only from region to region, but was different at different time scale and different time periods, but had negative effect on the whole.
摘要:在全球气候变暖的背景下,极端降水已经引起了一系列问题。由于“一带一路”主体水资源区(MWR)时空降水条件复杂,为了全面分析其极端降水特征,选取了351个气象站的日降水观测资料用于分析。选用了气候变化监测与指数专家组(ETCCDI)推荐的极端降水指标,使用Mann-Kendall检验分析其变化趋势,并利用小波分析方法计算了4个典型极端降水指数的周期特征。为了进一步分析极端降水指数与全球气候异常的关系,选取南方涛动指数(SOI)和北极涛动指数(AO)作为气候指数,研究极端降水指数与大气振荡的遥相关关系。结果表明:(1) 极端降水的频率和强度均有所上升,MWR的气候条件更加湿润;(2) 4个典型的极端降水指数表现表现出多重和重叠的周期,并以23-32 a周期最为普遍;(3)大尺度大气环流与MWR的遥相关关系因地而异,且在不同时间尺度和不同时期有所不同,但是整体来说具有负面影响。
图文导读:
(一)“一带一路”主体水资源区及站点分布情况
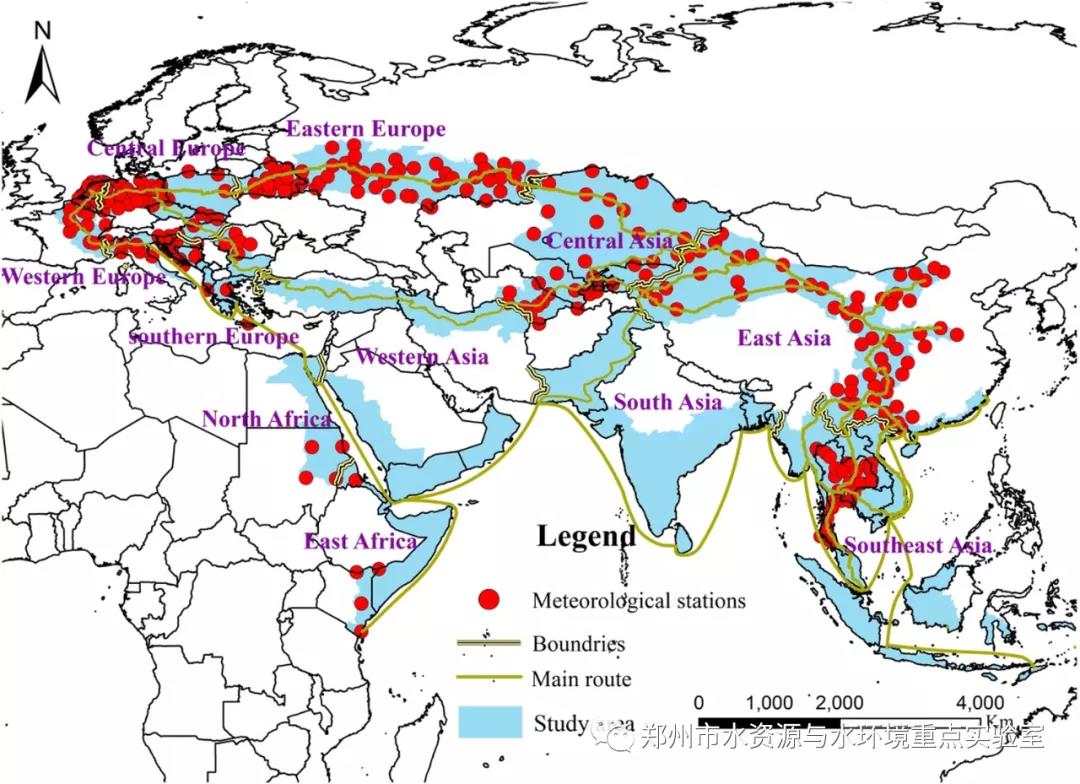
本研究对主体水资源区的极端降水特征进行评估,研究区域可分为11个区域:中欧,南欧,东欧,西欧,中亚,西亚,东亚,南亚,东南亚,北非和东非。但是由于北非和东非只有少数站点通过了质量控制,本研究不考虑这些站点。
(二)“一带一路”主体水资源区各站点极端降水指标的变化趋势
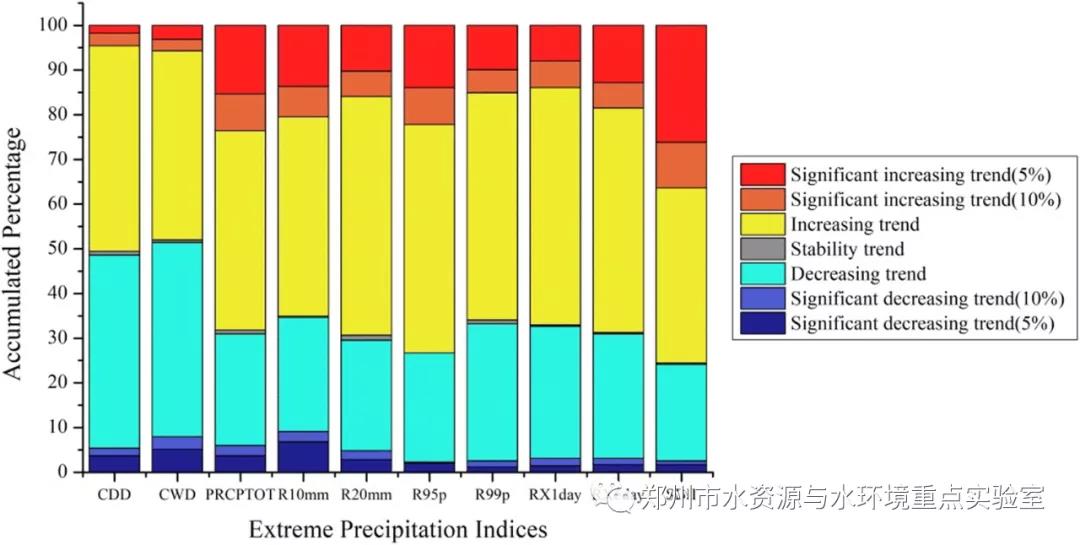
主体水资源区不同站点对于不同的降水指标,其变化趋势各不相同。只有CWD其下降趋势略高于增长趋势,其他9个指标增长趋势明显多于下降趋势且与其他指标相比SDII呈现显著增长趋势(10%)所占比例较大。
本研究以“一带一路”主体水资源区为研究区域,利用Mann-Kendall检验,评估了10个极端降水指标的变化趋势,并使用了小波分析方法分析极端降水事件的变化周期。为更好的揭示出极端降水事件变化的原因,研究其与气候变化之间的关系,我们分析了4个极端降水指标与SOI和AO等大气涛动现象的遥相关关系,本文结果如下:(1) 研究区不同极端降水指标分的空间分布模式有所不同,但是主要以积极趋势为主;(2) 整体来看在不同时间段内均有变化周期存在;(3)两个大气涛动现象对极端降水现象呈现出一定的抑制现象。
Qiting Zuo, Yixuan Diao*, Hao Lingang, Han Chunhui. ComprehensiveEvaluation of the Human-Water Harmony Relationship in Countries Along the"Belt and Road". Water Resources Management, 2020, 34(13),4019-4035.
DOI: 10.1007/s11269-020-02632-2
Qiting Zuo, Yuxin Song, Haojie Wang*, Jialu Li,Chunhui Han. . Spatial variations of extreme precipitation events andattribution analysis in the main water resource area of the Belt and RoadInitiative[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2021:1-20.
DOI: 10.1007/s00704-021-03556-6
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00704-021-03556-6

